随机数的使用你是不是经常用到?我们在进行运行SpringBoot单元测试时一般不会指定应用程序启动时的端口号,可以在application.properties文件内配置server.port的值为${random.int(10000)},代表了随机使用0~10000的端口号。
既然这种方式使用这么方便,那你知道${random.int}是通过什么方式实现的吗?
推荐阅读
概述
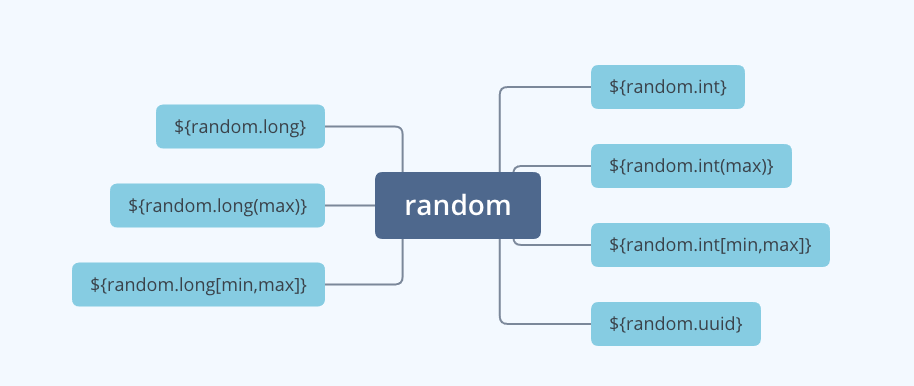
配置文件方式 在我们分析源码之前,我们先来看看${random.xxx}具体提供了哪几种的随机配置。
int随机数 使用${random.int}方式配置,结果从int的最大值、最小值中间产生,int的最小值为-2147483648,最大值为2147483647,配置如下所示:
1 2 server: port: ${random.int}
int范围随机数 使用${random.int(10000)}方式配置,这种方式我们可以指定随机数的最大值 ,当然不能超过2147483647,配置如下所示:
1 2 server: port: ${random.int(10000)}
注意事项:${random.int(10000)}随机数的值将会在0~10000之间产生,配置的最大值必须为正整数 ,
如果需要指定随机数的最小值,可以使用${random.int[100,200]}方式配置,这样只会从100~200之间产生随机数(包括最小值,不包括最大值)。
long随机数 使用${random.long}方式配置,结果会从long的最大值、最小值中间产生,long的最小值为-9223372036854775808,最大值为9223372036854775807,配置方式如下所示:
1 2 config: longValue: ${random.long}
long范围随机数 使用${random.long(10000)}方式配置,我们可以指定0~9223372036854775807之间的任意数值作为随机的最大上限,配置方式如下所示:
1 2 config: maxLongValue: ${random.long(102400)}
如果需要指定最小值,可以使用${random.long[1024,2048]}方式配置,这样只会从1024~2048中产生随机数(包括最小值,不包括最大值)。
uuid随机数 uuid因为它的唯一性,应该是我们平时开发中比较常用到的。
SpringBoot也为我们考虑到了这一点,我们只需要使用${random.uuid}就可以获得一个随机的uuid字符串,配置方式如下所示:
1 2 config: uuid: ${random.uuid}
@Value方式 如果在我们在编码中需要用到随机数的生成,${random}是支持注入使用的,主要还是因为它的实现继承自PropertySource。
我们可以在Spring IOC所管理的类内直接使用@Value注解进行注入使用,如下所示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 @Value("${random.uuid}") private String uuid;@Value("${random.int(1000)}") private int maxInt;@Value("${random.long(102400)}") private long maxLong;
源码解析 我们之所以可以这么方便的使用随机数,都归功于SpringBoot为我们提供了一个名为RandomValuePropertySource的PropertySource实现类,该实现类位于org.springframework.boot.env包内,该类部分源码如下所示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 public class RandomValuePropertySource extends PropertySource <Random> { private static final String PREFIX = "random." ; private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(RandomValuePropertySource.class); @Override public Object getProperty (String name) { if (!name.startsWith(PREFIX)) { return null ; } if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Generating random property for '" + name + "'" ); } return getRandomValue(name.substring(PREFIX.length())); } private Object getRandomValue (String type) { if (type.equals("int" )) { return getSource().nextInt(); } if (type.equals("long" )) { return getSource().nextLong(); } String range = getRange(type, "int" ); if (range != null ) { return getNextIntInRange(range); } range = getRange(type, "long" ); if (range != null ) { return getNextLongInRange(range); } if (type.equals("uuid" )) { return UUID.randomUUID().toString(); } return getRandomBytes(); } private String getRange (String type, String prefix) { if (type.startsWith(prefix)) { int startIndex = prefix.length() + 1 ; if (type.length() > startIndex) { return type.substring(startIndex, type.length() - 1 ); } } return null ; } private int getNextIntInRange (String range) { String[] tokens = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(range); int start = Integer.parseInt(tokens[0 ]); if (tokens.length == 1 ) { return getSource().nextInt(start); } return start + getSource().nextInt(Integer.parseInt(tokens[1 ]) - start); } private long getNextLongInRange (String range) { String[] tokens = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(range); if (tokens.length == 1 ) { return Math.abs(getSource().nextLong() % Long.parseLong(tokens[0 ])); } long lowerBound = Long.parseLong(tokens[0 ]); long upperBound = Long.parseLong(tokens[1 ]) - lowerBound; return lowerBound + Math.abs(getSource().nextLong() % upperBound); } }
当我们使用${random.xxx}这种方式获取随机数时,无论是配置文件方式还是@Value方式都会通过org.springframework.boot.env.RandomValuePropertySource#getProperty方法来获取对应类型的随机数。
注意事项:RandomValuePropertySource在继承PropertySource时泛型类型为Random,java.util.Random类内包含了全部的随机生成逻辑,该类由java提供,有兴趣可以研究下源码。
总结 SpringBoot内的配置都是通过ConfigurablePropertyResolver属性配置解析器来获取的,而该类的实例化在AbstractEnvironment内,我们通过AbstractEnvironment#getProperty(java.lang.String)方法可以获取由多个PropertySource实现类提供的属性配置。





 OAuth vs SAML vs OpenID
OAuth vs SAML vs OpenID




